- You have no items in your shopping cart
- Subtotal: $0.00
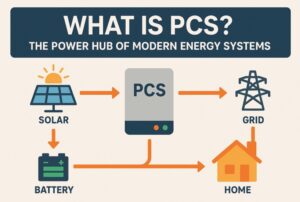
A bidirectional inverter is an advanced type of inverter that can both convert DC (direct current) to AC (alternating current) and AC to DC. Unlike traditional inverters, which typically operate in a single direction (DC to AC), bidirectional inverters operate in both directions, enabling two-way energy flow.
This capability is especially crucial in modern energy storage systems (ESS) and grid-tied renewable energy setups, where energy might need to be stored in batteries and sent back to the grid when needed.
How Does a Bidirectional Inverter Work?
At its core, a bidirectional inverter consists of power electronic components like IGBTs or MOSFETs that can switch modes based on real-time control systems. It operates in two main modes:
1. Inverter Mode (DC to AC)
- Converts DC power from batteries or solar panels into AC power for use in homes, industries, or the grid.
2. Rectifier Mode (AC to DC)
- Converts AC power from the grid into DC power to charge batteries or power DC loads.
This two-way power flow makes it possible to:
- Store excess renewable energy during the day.
- Feed stored energy back to the grid during peak demand.
- Charge batteries during off-peak hours (when electricity is cheap).
Key Features of Bidirectional Inverters
- Dual Power Flow: Supports both AC-to-DC and DC-to-AC conversions.
- Smart Control: Advanced firmware for energy flow management.
- Grid Interaction: Synchronizes with utility grids for energy export/import.
- Battery Integration: Optimized for working with Lithium-ion or other battery systems.
- High Efficiency: Often >95% conversion efficiency.
Uses of Bidirectional Inverters
Bidirectional inverters are found in a wide range of modern energy systems. Here are some of the most common applications:
1. Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
- Charge batteries using grid or solar power.
- Discharge power back to homes or grids during peak load.
- Key component in both residential and commercial storage solutions.
2. Microgrids
- Manage power flow between solar panels, battery storage, and the utility grid.
- Maintain power stability during grid outages.
3. Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging
- Enables Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) systems where EVs can return stored power to the grid.
- Allows smart charging during low-demand periods and discharging during high-demand.
4. Renewable Energy Systems
- Integrate solar, wind, or hybrid energy systems with grid and storage.
- Help regulate fluctuating power from intermittent sources.
5. Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)
- Maintain backup power and automatically switch modes during outages.
- Recharge batteries when normal power is available.
Benefits of Using a Bidirectional Inverter
✅ Maximizes Energy Efficiency
By enabling two-way power flow, energy can be stored and utilized smartly without waste.
✅ Supports Grid Stability
Can inject power back to the grid when demand is high, helping utilities manage peak loads.
✅ Reduces Energy Costs
Allows users to consume energy when it’s cheap and sell it back during high-rate periods.
✅ Enables Smart Energy Management
Advanced monitoring and control systems help optimize energy usage and storage.
✅ Eco-Friendly
Supports renewable integration and reduces dependency on fossil fuel-based grid energy.
✅ Future-Ready
Compatible with smart homes, EVs, and evolving grid systems.
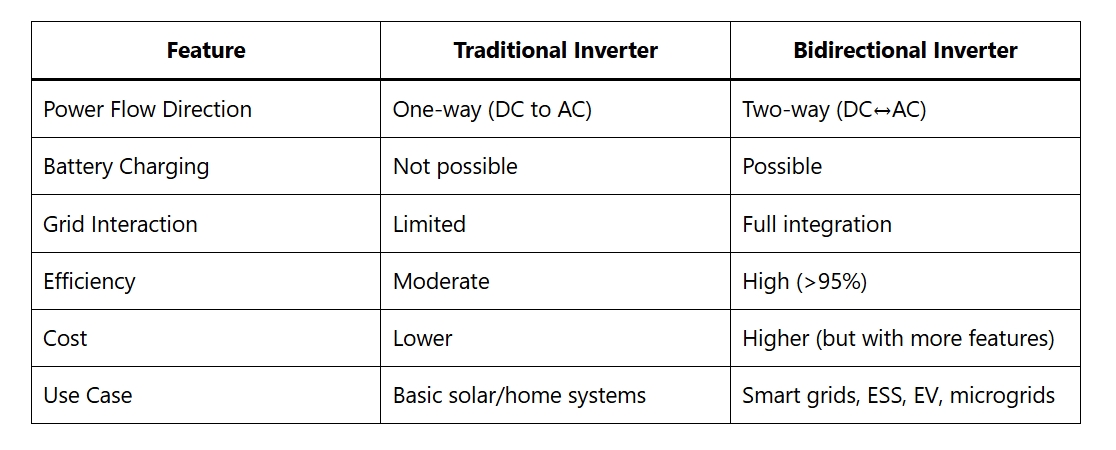
Bidirectional Inverter vs Traditional Inverter
| Feature | Traditional Inverter | Bidirectional Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Power Flow Direction | One-way (DC to AC) | Two-way (DC↔AC) |
| Battery Charging | Not possible | Possible |
| Grid Interaction | Limited | Full integration |
| Efficiency | Moderate | High (>95%) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher (but with more features) |
| Use Case | Basic solar/home systems | Smart grids, ESS, EV, microgrids |
Do You Need a Bidirectional Inverter?
You may need a bidirectional inverter if:
- You have a solar system with energy storage and want to feed excess energy back to the grid.
- You operate a microgrid or off-grid project.
- You want to use EV batteries as backup power.
- You’re building a commercial energy storage system.
- You aim to reduce energy bills through peak shaving and load shifting.
If you only use solar power during the day and don’t store or export power, a regular inverter might suffice. But for dynamic energy control and future expansion, a bidirectional inverter is the better choice.
Challenges and Considerations
While bidirectional inverters are highly capable, here are some considerations:
- Higher Initial Cost: They are more expensive than single-direction inverters.
- Complex Installation: Requires proper design, integration, and compliance with grid codes.
- Regulatory Barriers: Some utilities may have restrictions on energy export.
However, with increasing demand for grid resilience and sustainable energy, They are quickly becoming mainstream.
Future of Bidirectional Inverters
As more countries push for net-zero goals and increased renewable energy adoption, bidirectional inverters will play a critical role in:
- Smart Grid Development
- Decentralized Energy Systems
- VPPs (Virtual Power Plants)
- EV Integration
- Home and Commercial Energy Automation
They are not just inverters anymore — they’re smart power managers.
FAQs
❓ What is the main difference between a regular inverter and a bidirectional inverter?
A regular inverter only converts DC to AC. A bidirectional inverter can convert both DC to AC and AC to DC, enabling battery charging and energy export to the grid.
❓ Can I use a bidirectional inverter with solar panels?
Yes, they are commonly used in solar systems with battery storage and grid-tied configurations.
❓ Are bidirectional inverters expensive?
They have a higher upfront cost than traditional inverters but offer greater flexibility and savings in the long run.
❓ Is a bidirectional inverter suitable for home use?
Yes, especially if your home has solar panels, batteries, or electric vehicles. It gives better control over your energy flow.
Final Thoughts
A bidirectional inverter is more than just a fancy piece of tech — it’s the heart of modern, intelligent energy systems. Whether you’re managing a home solar setup, a commercial energy storage plant, or an EV fleet, these inverters provide the flexibility, efficiency, and control that today’s dynamic energy landscape demands.
Ready to upgrade your energy system?
Make sure to choose a reliable bidirectional inverter that matches your project size, battery type, and local grid requirements.