- You have no items in your shopping cart
- Subtotal: $0.00

[ad_1]
Researchers from Texas A&M University have developed a way to create better batteries for a better future by imagining nanoscale flaws in current models.
Energy is a fundamental concern when it comes to the development of any technology. Hopefully it’s a space shuttle or even a new mobile device. Energy storage systems are becoming complex with their size and growing requirements. Researchers are trying to develop a better option by introducing various new manufacturing methods as well as new energy storage methods.
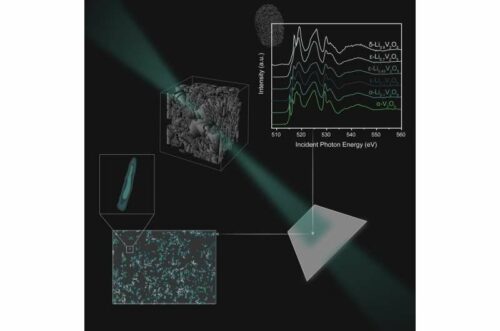
An international team of experts, led by researchers from Texas A&M University, combined powerful imaging techniques and large data sets to better understand why lithium-ion batteries fail and how to fix them. carefully. “A technical gap that exists today is that we do not fully understand what is happening at the nanoscale and for that we are working closely with a Canadian Light Source to use many different imaging techniques to investigate further,” said by David Santos, a Texas A&M chemistry Ph.D. graduate and former member of Texas A&M chemist Sarbajit Banerjee’s research group.
The researchers were able to visualize the defects and map defects that occur inside the batteries using the SM beamline at the Canadian Light Source (CLS)—located at the University of Saskatchewan (UofS). “The X-ray tools at the Canadian Light Source are great for eavesdropping on batteries, and the little secret conversations that ions have and finding out what makes them fail,” he said. Banerjee.
The team is interested in identifying in real time the faults that occur which will allow them to measure the complex relationship between the battery’s materials, its shape, and the chemical reactions that occur inside. Achieving this goal will allow researchers to proactively address design failures.
The chemical and mechanical changes that occur throughout the life of the battery can also lead to defects—such as cracks in the ceramic mug—that affect its longevity. Santos says that the disadvantages that affect the performance of a battery are also linked to safety risks and have a significant impact on the environment. More efficient batteries help reduce waste and help us transition to a greener grid.
Reference: David A. Santos et al, Multivariate hyperspectral data analytics across length scales to assess compositional, phase, and strain heterogeneities in electrode materials, Standards (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.pattern.2022.100634
[ad_2]
Source link



