- You have no items in your shopping cart
- Subtotal: $0.00

Electricity powers our modern world, from household gadgets to entire industries. However, not all electrical systems operate the same way. While many power sources like batteries and solar panels provide Direct Current (DC), our appliances require Alternating Current (AC). That’s where an inverter becomes a vital tool.
What is an Inverter?
An inverter is an electrical device that converts Direct Current (DC) into Alternating Current (AC). It allows you to use DC power sources—like solar panels or batteries—to run standard AC appliances. This conversion makes inverters essential in both residential and commercial energy systems.
How Does an Inverter Work?
The process begins with a DC power source, such as a solar panel or battery. The inverter then uses electronic switching components (like MOSFETs or IGBTs) to rapidly turn the DC signal on and off, mimicking an AC waveform.
The key components in the process:
- DC Input – from a battery, solar panel, or fuel cell
- Oscillator Circuit – generates a high-frequency pulse
- Switching Unit – modulates the signal using transistors
- Filter/Transformer – smooths the waveform into usable AC
- AC Output – provides power to your appliances
The result: clean, reliable AC power that can run anything from lights to refrigerators.
Types of Inverters
Inverters can be categorized based on waveform output, integration with other systems, and electrical phase. Let’s explore these classifications in detail.

A. Based on Output Waveform
1. Pure Sine Wave Inverter
- Produces a smooth, grid-quality sine wave
- Ideal for sensitive electronics like laptops, TVs, and medical equipment
- More efficient and safer but slightly costlier
2. Modified Sine Wave Inverter
- Creates a step-like waveform
- Suitable for simple appliances like lights or fans
- May cause noise or reduce lifespan in some electronics
3. Square Wave Inverter
- Its a Basic and low-cost type
- Only works well with resistive loads like heaters
- Not recommended for modern appliances
B. Based on Application or Source Integration
1. Stand-Alone Inverter
- Operates independently with a battery backup
- Commonly used in homes and shops during power outages
2. Grid-Tie Inverter
- Connects directly to the utility grid
- Converts solar power and feeds it back to the grid
- No battery backup included
3. Hybrid Inverter
- Combines solar, battery, and grid input
- Supports energy storage and grid interaction
- Ideal for smart homes and off-grid systems
C. Based on Electrical Phase
1. Single-Phase Inverter
- Supplies power through one alternating phase
- Standard in homes and small businesses
- Voltage Output: Typically 220V–240V
- Applications: TVs, lights, fans, refrigerators
2. Three-Phase Inverter
- Delivers power through three alternating currents
- Suited for high-load industrial or commercial setups
- Voltage Output: 380V–415V
- Applications: Motors, HVACs, lifts, factory machines
3. Split Phase Inverter (110V/220V Output)
A Split Phase Inverter is designed for use in countries like the United States, Canada, and parts of Latin America, where homes require both 110V and 220V simultaneously.
Here’s how it works:
- It produces two 110V outputs that are 180° out of phase.
- When combined, these deliver 220V across both lines.
- Between either line and neutral, you still get standard 110V.
This setup powers both low and high-voltage appliances without needing two separate systems.
- Voltage Output: 110V and 220V
- Applications: U.S. homes, RVs, tiny homes, solar cabins
- Advantages:
- Runs both 110V and 220V appliances
- Great for solar power and off-grid systems
- Eliminates the need for dual inverter units
⚡ Why It Matters: If you live in North America and want to power your home with solar and battery backup, a split-phase inverter is often the most flexible and efficient option.
Where Are Inverters Used?
Inverters are integrated across many fields for their flexibility and reliability. Here’s a look at common applications:
1. Residential Backup Systems
In areas with frequent blackouts, it provide uninterrupted power using batteries. They ensure your essential appliances like fans, routers, and refrigerators stay on.
2. Solar Energy Systems
Solar panels generate DC, which must be converted to AC using a solar inverter. This AC power is either used immediately or sent back to the grid in a grid-tie system.
3. Commercial and Industrial Applications
Industries use it to control motor speed, run conveyors, pumps, and even welders. It improves operational efficiency and equipment life.
4. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
EVs rely on it to convert battery DC into AC for the electric motor. Some EVs also include bi-directional inverters for vehicle-to-grid (V2G) power export.
5. Data Centers and Telecom
Critical infrastructure like telecom towers and data centers need uninterrupted power. It provides clean and stable backup during outages.
6. Off-Grid Cabins and Portable Power
From camping to remote cabins, inverters in portable power stations provide both 110V and 220V AC for tools, gadgets, and essential appliances.
Conclusion
Its much more than a backup power device—it’s a gateway that converts DC into usable AC for modern living. Whether you’re powering a small cabin, an entire home, or a factory, choosing the right type of it(single-phase, three-phase, or split-phase) is crucial for performance and safety.
✅ Pro Tip: Always size your inverter based on load requirements and choose the correct waveform and voltage output (especially if you need both 110V and 220V) for maximum efficiency.


[…] Inverter check every 5–10 years […]
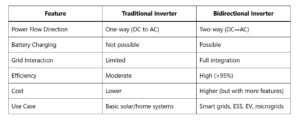
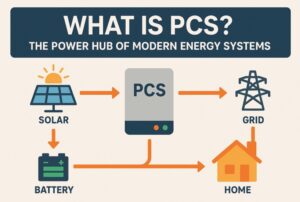
[…] people confuse PCS with inverters. Here’s the […]
[…] In modern energy systems, especially those involving solar, batteries, and smart grids, terms like inverter, bidirectional inverter, and PCS (Power Conversion System) often come up. While they may sound […]