- You have no items in your shopping cart
- Subtotal: $0.00
Inverter vs Bidirectional Inverter vs PCS: In modern energy systems, especially those involving solar, batteries, and smart grids, terms like inverter, bidirectional inverter, and PCS (Power Conversion System) often come up. While they may sound similar, they serve very different purposes depending on the system design.
If you’re working with renewable energy, battery energy storage systems (BESS), or hybrid systems, understanding these components is essential. Let’s break it down in simple terms.
🟢 What is an Inverter?
An inverter is an electronic device that converts DC (Direct Current) to AC (Alternating Current).
📌 Where is it used?
- Solar panels generate DC power.
- Homes and grids run on AC power.
- So, inverters are used in solar power systems, battery systems, and even small UPS units.
✅ Key Functions:
- Convert DC to AC.
- Match grid frequency and voltage.
- Supply AC power for homes and appliances.
🔻 Limitations:
- Most basic inverters are unidirectional – they can only convert DC to AC.
- They do not allow charging a battery from the grid or AC side.
🔁 What is a Bidirectional Inverter?
⚙️ How It Works:
- Converts DC to AC (to supply power).
- Converts AC to DC (to charge the battery from the grid or generator).
📌 Common Applications:
- Hybrid solar systems.
- Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS).
- EV charging stations.
- Microgrids.
✅ Benefits:
- Enables energy arbitrage – store power when it’s cheap, use it when expensive.
- Supports backup power and grid interaction.
- Allows solar self-consumption optimization.
🔌 What is PCS (Power Conversion System)?
⚙️ What It Does:
- Manages high-voltage DC and AC conversion.
- Includes communication with EMS (Energy Management System) and BMS (Battery Management System).
- Provides frequency regulation, voltage control, and reactive power support.
🔍 Key Features:
- High efficiency (over 97% in many systems).
- Handles hundreds of kW to MW scale power.
- Works with grid-tied and off-grid applications.
- Advanced protection & control systems built-in.
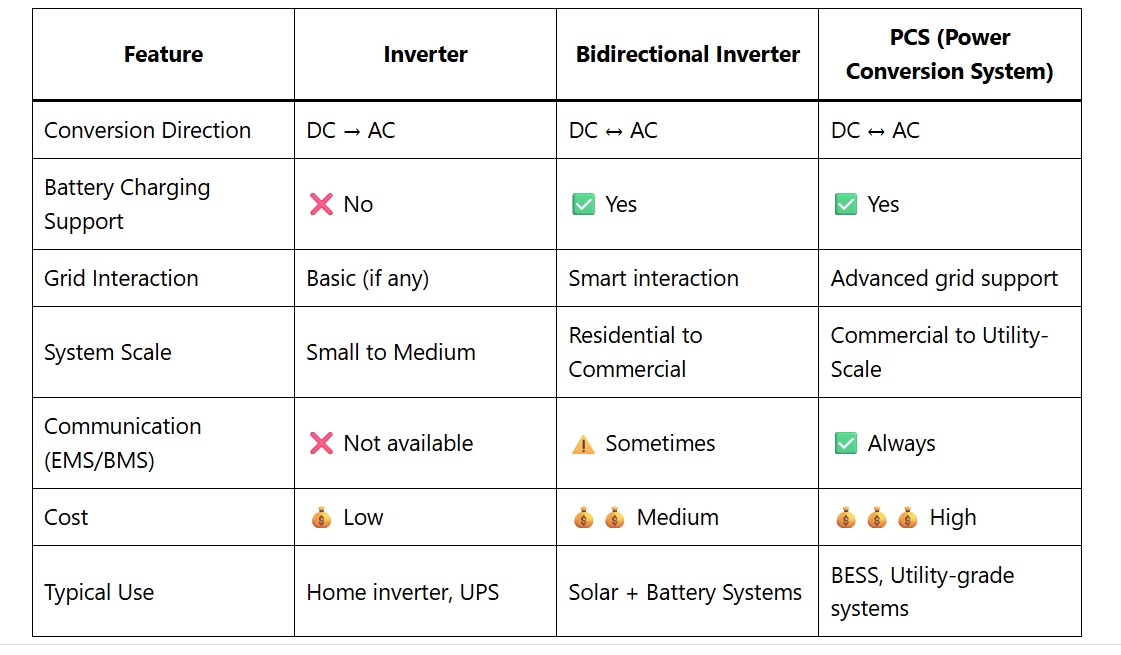
🔄 Comparison Table
| Feature | Inverter | Bidirectional Inverter | PCS (Power Conversion System) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conversion Direction | DC → AC | DC ↔ AC | DC ↔ AC |
| Battery Charging Support | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Grid Interaction | Basic (if any) | Smart interaction | Advanced grid support |
| System Scale | Small to Medium | Residential to Commercial | Commercial to Utility-Scale |
| Communication (EMS/BMS) | ❌ Not available | ⚠️ Sometimes | ✅ Always |
| Cost | 💰 Low | 💰💰 Medium | 💰💰💰 High |
| Typical Use | Home inverter, UPS | Solar + Battery Systems | BESS, Utility-grade systems |
🎯 Which One Do You Need?
If you’re a homeowner:
A regular inverter or a bidirectional inverter is usually enough.
If you have solar + battery:
Use a bidirectional inverter to make the most of energy storage.
If you’re planning a large project:
For grid-connected energy storage, go for a PCS – it’s made for big jobs.
⚡ Real-World Example
Imagine a solar farm with battery storage:
- Inverter: Only useful if you’re converting solar DC to supply AC power to a load.
- Bidirectional Inverter: Lets you charge and discharge a battery but limited in scale.
- PCS: Controls how much battery power goes to the grid, takes grid signals, balances the frequency, and operates under grid codes.
🧠 Final Thoughts
Choosing between an inverter, a bidirectional inverter, and a PCS depends on:
- Your system size,
- The type of energy storage,
- And your grid interaction needs.
PCS is the backbone of smart, scalable, and flexible energy storage infrastructure. While basic inverters are great for homes, the world of energy is moving toward intelligent bidirectional systems that can do more.
🔎 FAQs
❓ Can a regular inverter charge a battery?
No. Most regular inverters are unidirectional. You need a bidirectional inverter or PCS to charge and discharge batteries.
❓ Is PCS only for large systems?
Mostly yes. PCS is ideal for commercial and utility-scale BESS and smart grid applications.
❓ What’s the difference between PCS and hybrid inverter?
A hybrid inverter is a type of bidirectional inverter for homes and small businesses. PCS is designed for higher power levels and advanced grid compliance.





[…] power, a regular inverter might suffice. But for dynamic energy control and future expansion, a bidirectional inverter is the better […]