- You have no items in your shopping cart
- Subtotal: $0.00
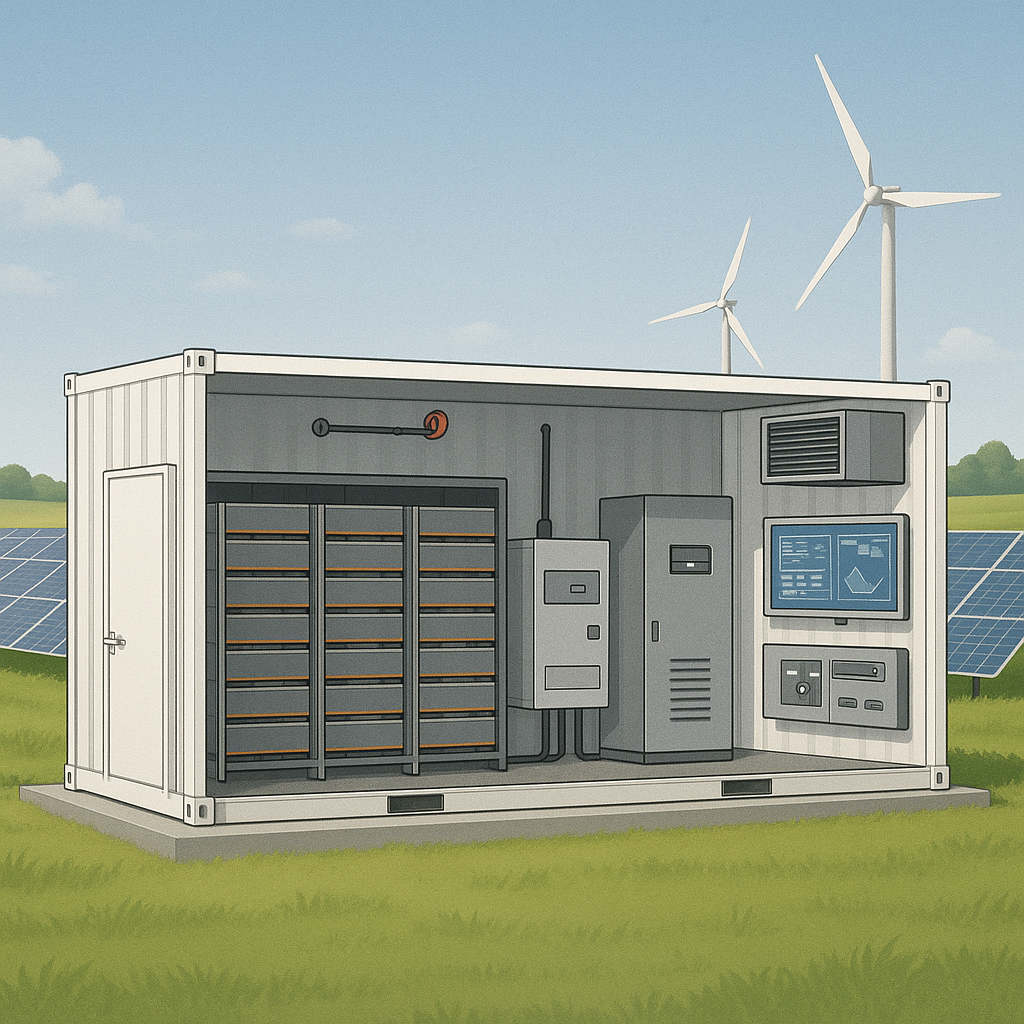
As the world shifts toward clean and reliable energy, Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) have become a cornerstone of modern energy infrastructure. But what exactly makes up a BESS and Key components of BESS
In this blog post, we’ll explore the key components of BESS, including battery modules, Battery Management System (BMS), Power Conversion System (PCS), Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA), Energy Management System (EMS), fire protection, HVAC, and more.
Each Key components of BESS plays a vital role in ensuring the safety, efficiency, and performance of the entire system.

1. Battery Modules
Function:
Battery modules are the heart of a BESS. They store the electrical energy that is later used to support grid demands, reduce peak loads, or provide backup power. A module consists of multiple battery cells—usually lithium-ion—arranged in a compact form.
Key Features:
- Assembled in series/parallel to meet energy requirements
- Integrated sensors for temperature and voltage monitoring
- Modular architecture for scalability
Advantages:
- High Energy Density: Stores more power in a smaller footprint
- Long Lifecycle: Can withstand thousands of charge/discharge cycles
- Flexible Configuration: Easily integrated into racks, packs, and strings
- Safe Design: Many modules include built-in protective circuits
Popular Chemistries:
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP): High thermal stability
- Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC): High energy density
- Sodium-ion (emerging): Cost-effective and thermally resilient
2. Battery Management System (BMS)
Responsibilities:
- Monitors voltage, current, and temperature of each cell
- Balances charge levels across cells
- Detects and isolates faults
- Controls charging and discharging cycles
Advantages:
- Safety Assurance: Prevents overheating and overcharging
- Extended Battery Life: Maintains health of individual cells
- Real-Time Monitoring: Enables system alerts and remote diagnostics
- Data Logging: Supports performance analysis and maintenance planning
3. Power Conversion System (PCS)
Main Components:
- Bidirectional inverter/converter
- Transformer (for grid compliance)
- Grid protection relays
Advantages:
- Bi-Directional Flow: Enables charging and discharging
- Grid Integration: Maintains voltage and frequency standards
- Black Start Capability: Restarts the system without external power
- Efficiency: Reduces energy loss during conversion
4. Energy Management System (EMS)
Function:
The EMS is the brains of the operation, coordinating when and how energy is stored or released. It supports energy optimization strategies like time-of-use pricing, peak shaving, and renewable integration.
Features:
- Real-time data analytics and forecasting
- Interfaces with SCADA, PCS, and external signals
- Supports demand response and virtual power plant (VPP) strategies
Advantages:
- Optimized Dispatch: Uses energy when it’s most cost-effective
- Grid Support: Enables frequency and voltage regulation
- Renewable Integration: Smooths output from solar and wind systems
- Economic Benefit: Reduces electricity bills and increases ROI
5. Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA)
Key Features:
- Graphical dashboards for visualization
- Alarm management and fault reporting
- Historical data logging for trends
- Secure remote access for operators
Advantages:
- Operational Transparency: Full visibility into system health
- Faster Response: Early detection of anomalies
- Remote Management: Efficient system control without on-site personnel
- Predictive Maintenance: Reduces unplanned downtime
6. Fire Protection System
Function:
Safety is paramount in any BESS. The fire protection system is designed to detect, suppress, and contain fires, especially from lithium-ion batteries prone to thermal runaway.
System Components:
- Smoke and gas detectors
- Thermal sensors
- Suppression agents (e.g., aerosol, gas, water mist)
- Emergency shutdown mechanisms
Advantages:
- Early Detection: Mitigates fire risks before escalation
- System Integrity: Protects equipment and personnel
- Compliance: Meets international safety standards (NFPA 855, UL 9540A)
- Insurance Friendly: Reduces risk profile for insurers
7. HVAC (Heating, Ventilation & Air Conditioning)
Function:
The HVAC system ensures the thermal stability of the battery modules and electronics. Batteries perform best within a narrow temperature range.
Functions Include:
- Cooling during high load or ambient heat
- Heating during cold starts
- Humidity control to avoid condensation
- Air filtration and dust prevention
Advantages:
- Performance Optimization: Keeps batteries within safe temperature limits
- Extended Life: Reduces thermal stress on battery cells
- Operational Continuity: Avoids shutdowns due to temperature excursions
- Redundancy: Dual systems for mission-critical reliability
8. Battery Racks and Enclosures
Function:
These house the battery modules and protect them from physical damage, weather, and unauthorized access.
Design Elements:
- Fire-rated metal enclosures
- Weatherproof seals (IP55 or above)
- Internal cable routing and thermal insulation
- Modular rack systems for easy maintenance
Advantages:
- Durability: Withstands environmental conditions
- Scalability: Easily adds new racks as energy needs grow
- Safety: Limits exposure to hazards
- Space Optimization: Maximizes storage density
9. Communication & Control Systems
Function:
These systems ensure seamless data exchange between different subsystems using protocols such as Modbus, CANbus, OPC-UA, and IEC 61850.
Advantages:
- Interoperability: Integrates devices from different manufacturers
- Real-Time Sync: Keeps all components updated with live data
- Remote Access: Enables cloud-based or control room operation
- Cybersecurity: Secures communication lines from external threats
10. Auxiliary Power Supply
Function:
Provides backup power to critical subsystems like the BMS, SCADA, HVAC, and fire protection when the main power is unavailable.
Components May Include:
- UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply)
- Diesel backup generator
- Battery-based emergency power packs
Advantages:
- Operational Continuity: Keeps systems running during outages
- System Safety: Maintains critical protections
- Disaster Recovery: Aids black start or emergency operation
- Regulatory Compliance: Meets uptime and safety requirements
Final Thoughts
A BESS is far more than just batteries in a box. It is a sophisticated, integrated system where every Key components of BESS —from the battery modules to the communication systems—must work in harmony.
Understanding these key components of BESS helps engineers, developers, and decision-makers design safer, smarter, and more reliable energy storage systems.
Whether you’re planning a commercial solar project, grid backup solution, or utility-scale storage, each component matters. Together, they make BESS a cornerstone of the clean energy future.